Theory
The Complete Musician - Steven G. Laitz
141~145
The foundation of tonal music (调性音乐)
tonic 主音
bar lines 小节线
measures 小节
accent 重音
staff 五线谱
clef 谱号
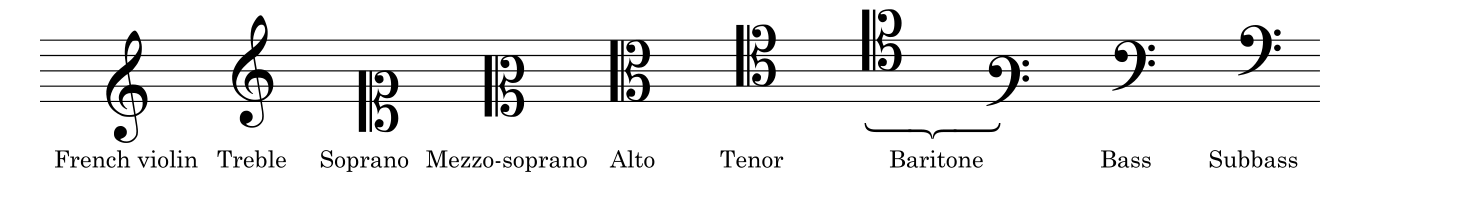
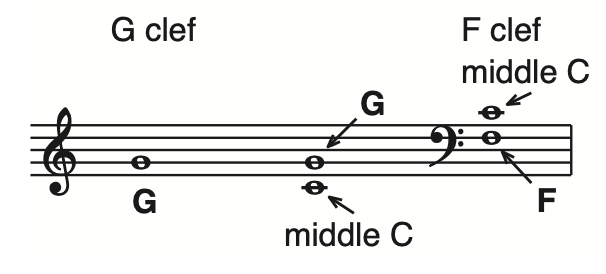
Ledger lines 加线(上加线,下加线)
Octave sign: 8va or 8vb
8va 演奏时高八度 8vb 演奏时低八度
Register 音区,如C3 to C5 是中音区,C6 to C8是高音区,但是相对并非绝对的概念
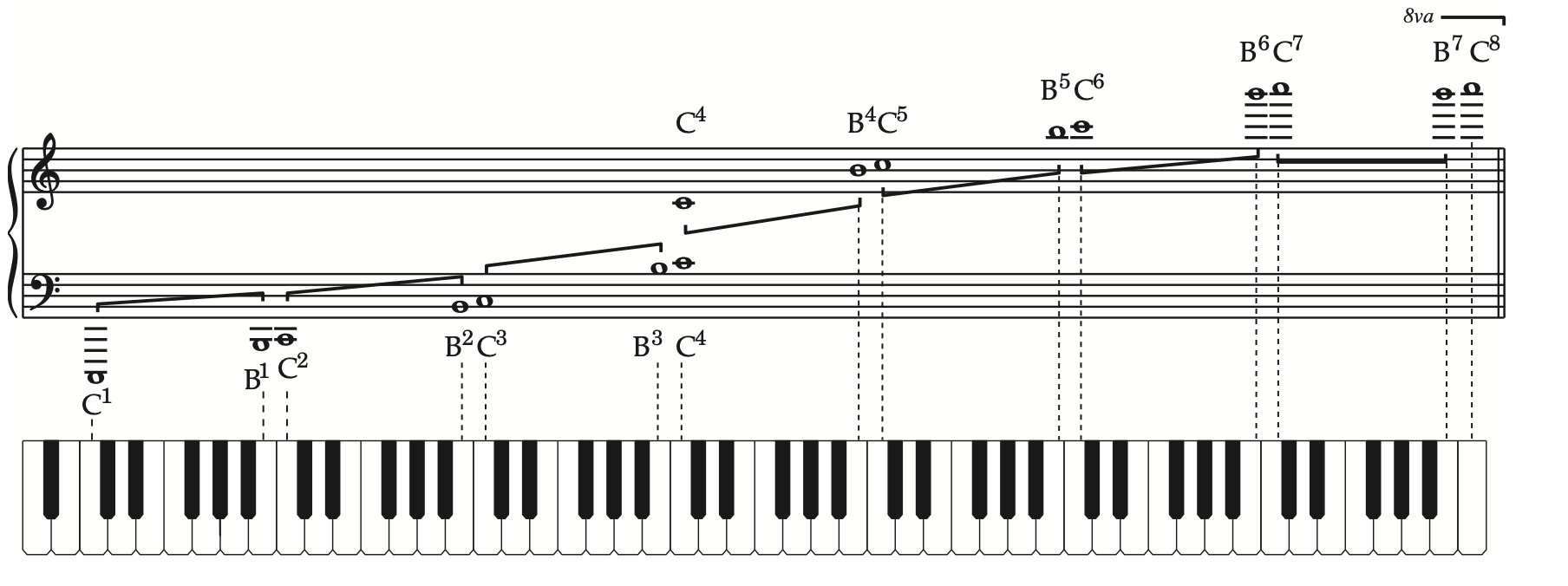
Pitch class 音高集合 其中所有的音高都剛好差整數倍的八度音
Interval 音程
Step 级进 Half step and Whole step
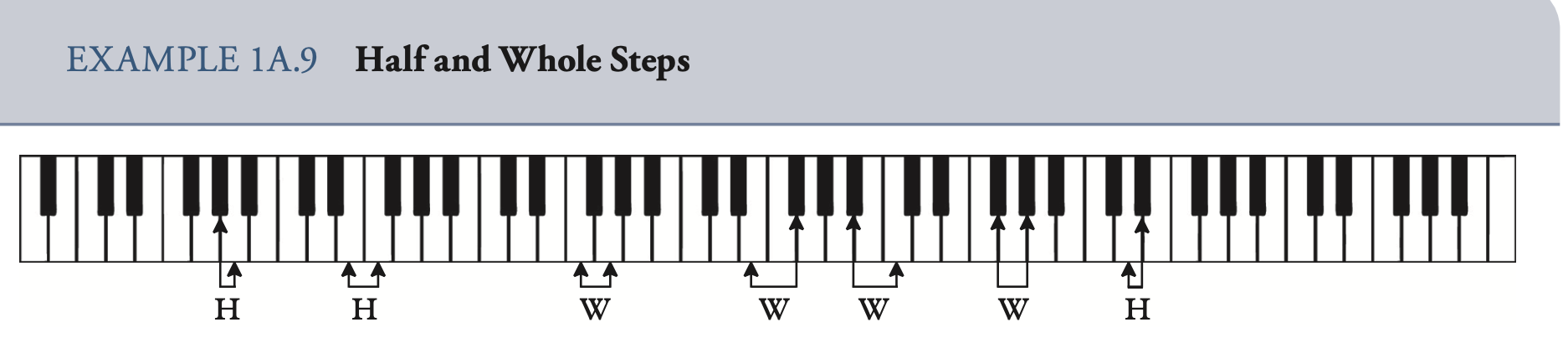
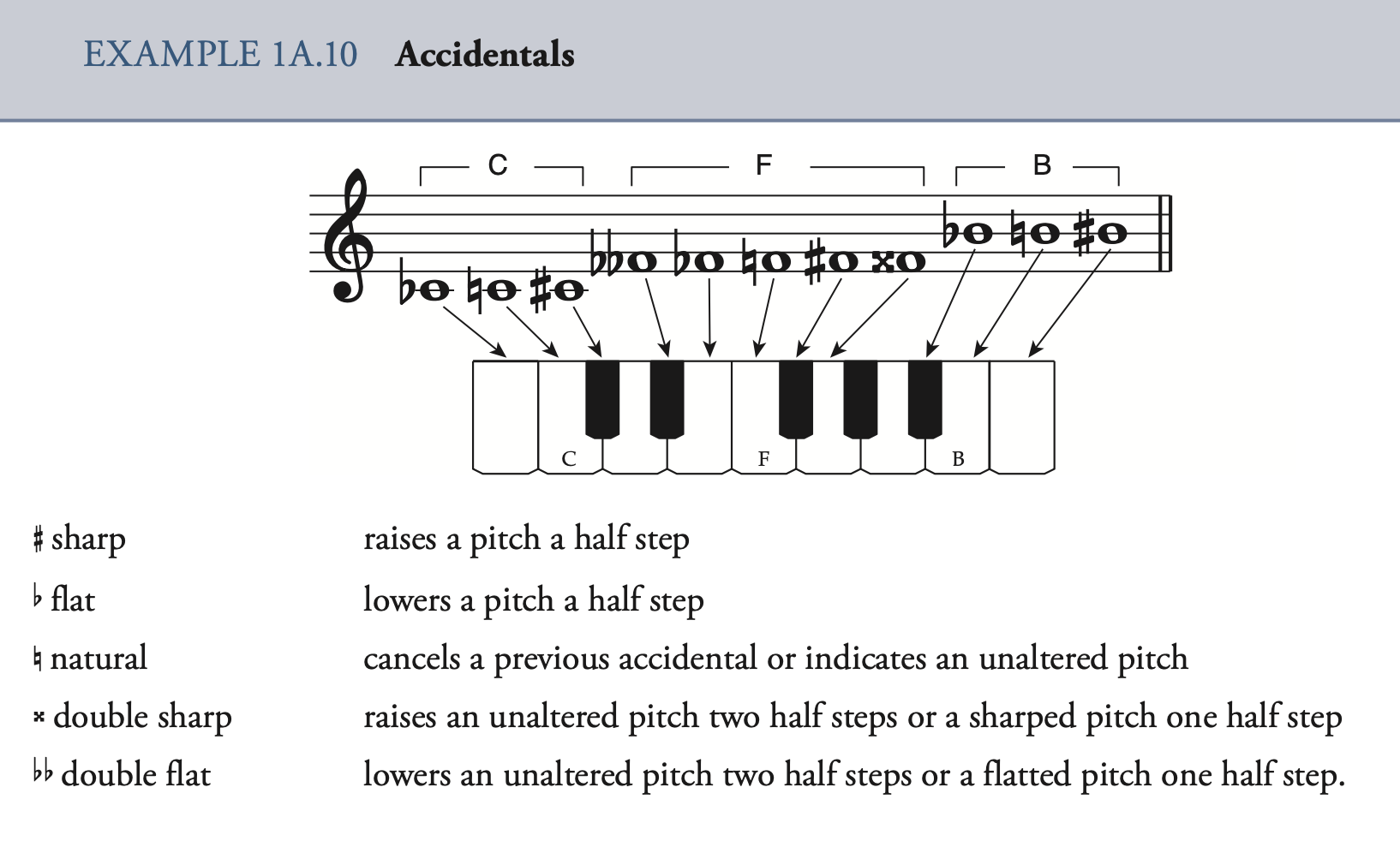
Accidental(s) 变音记号
Chromatic 半音的
Scale 音阶
diatonic scale 自然音阶
chromatic scale 半音阶
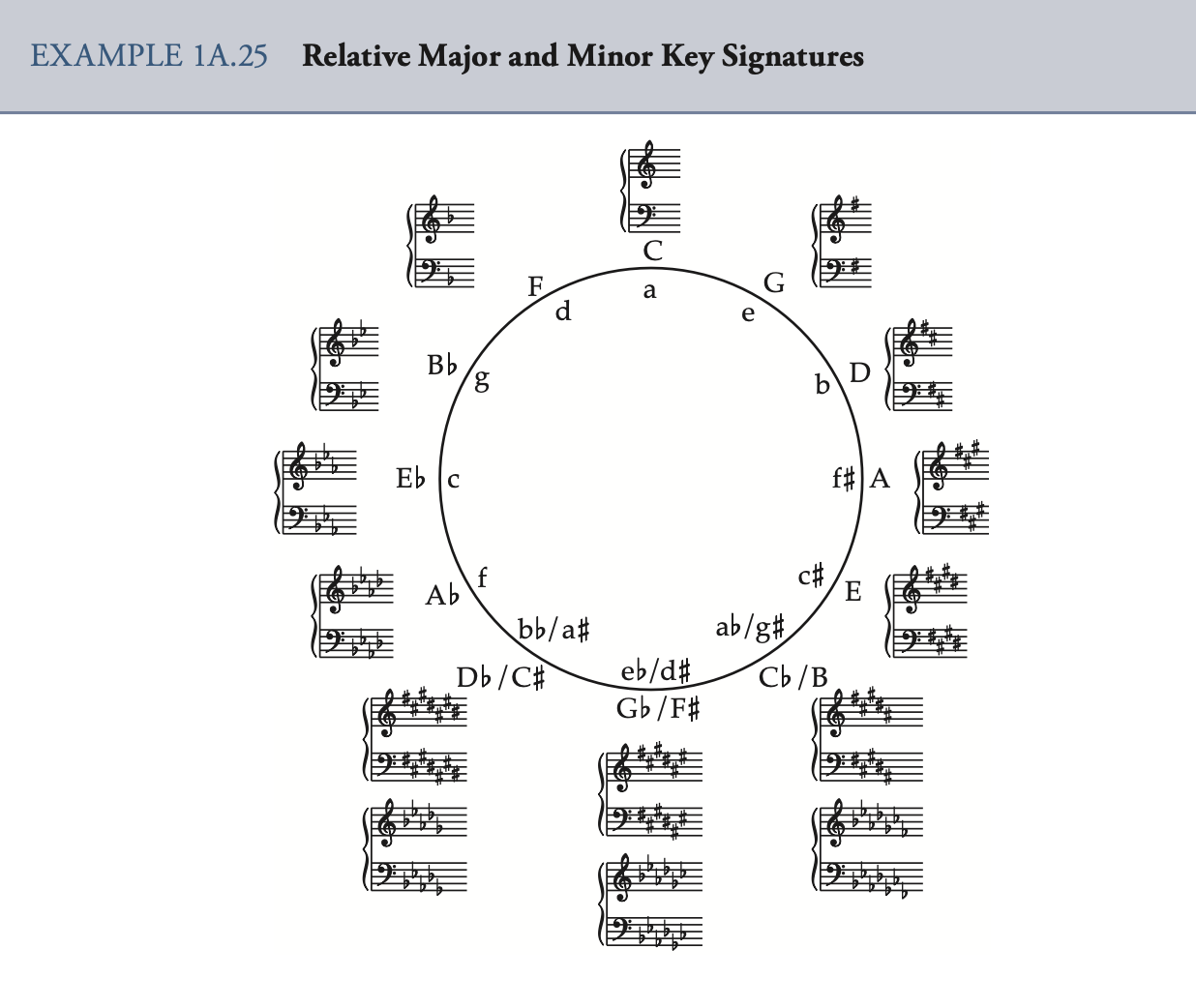
tonality 调性
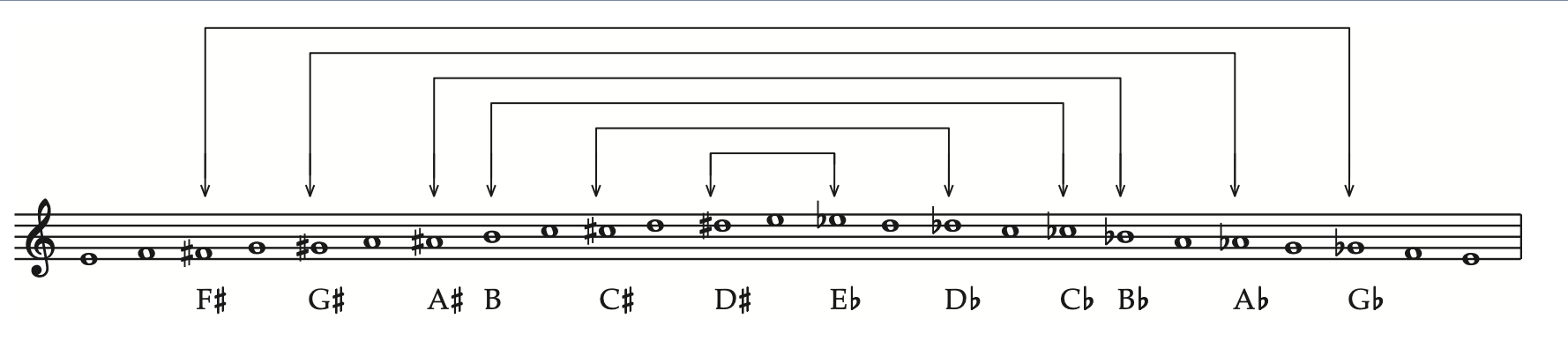
enharmonic 异名同音 音名不同而音高相同
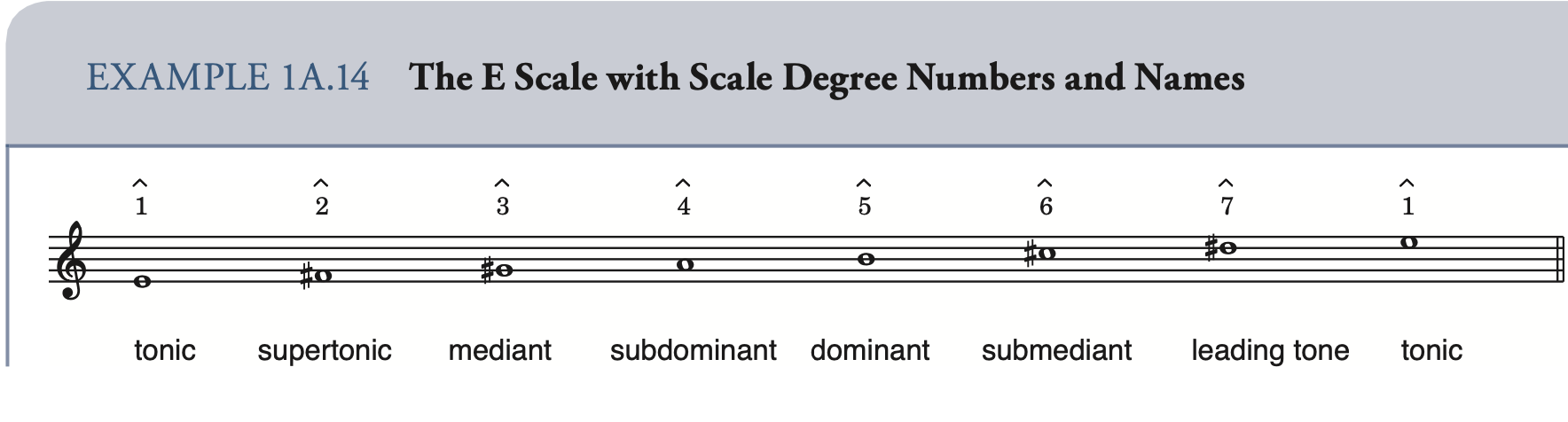
Tonic 主音
Supertonic 上主音
Mediant 中音
Subdominant 下属音
Dominant 属音
Submediant 下中音
Leading tone 导音(Subtonic)
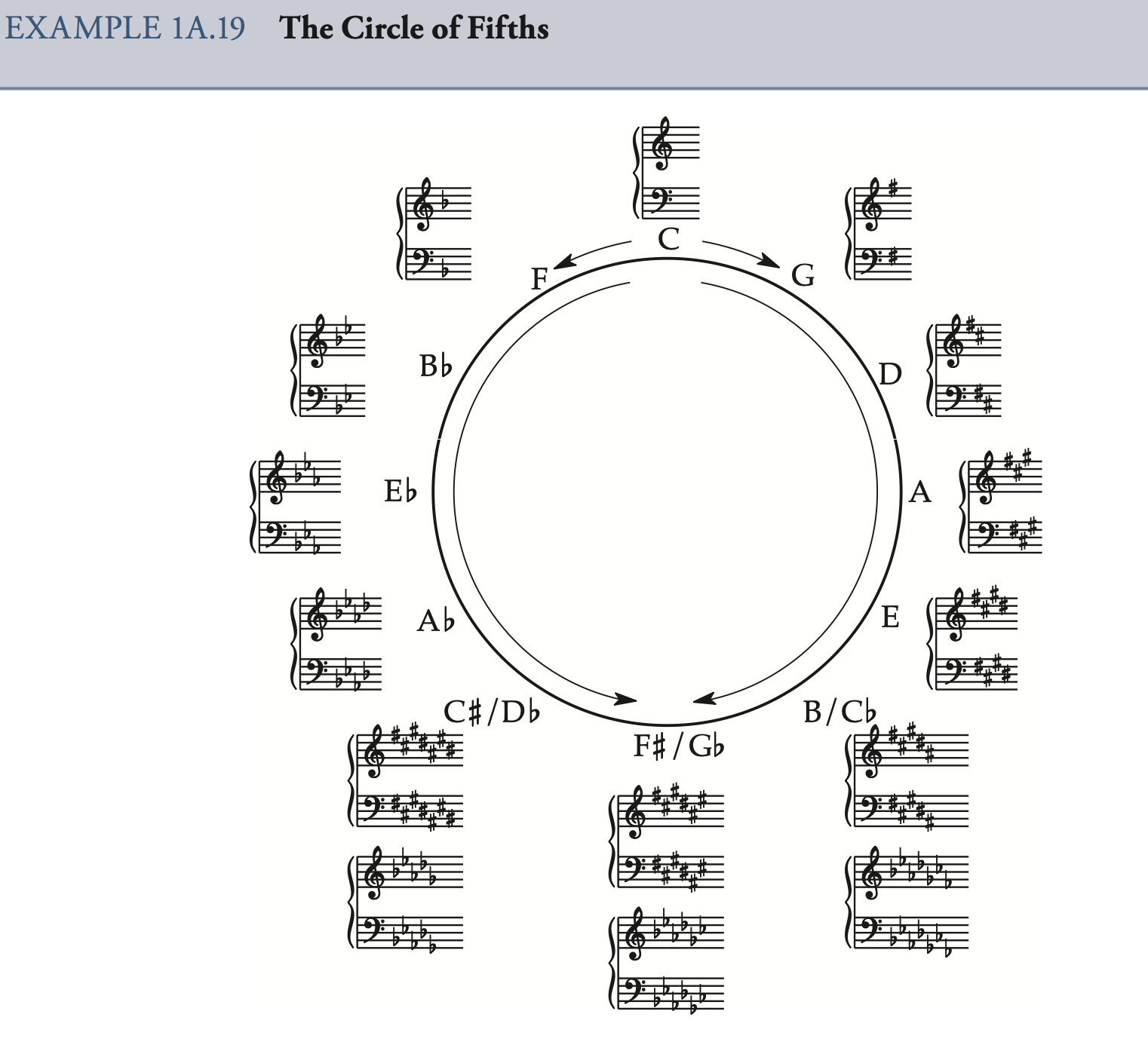
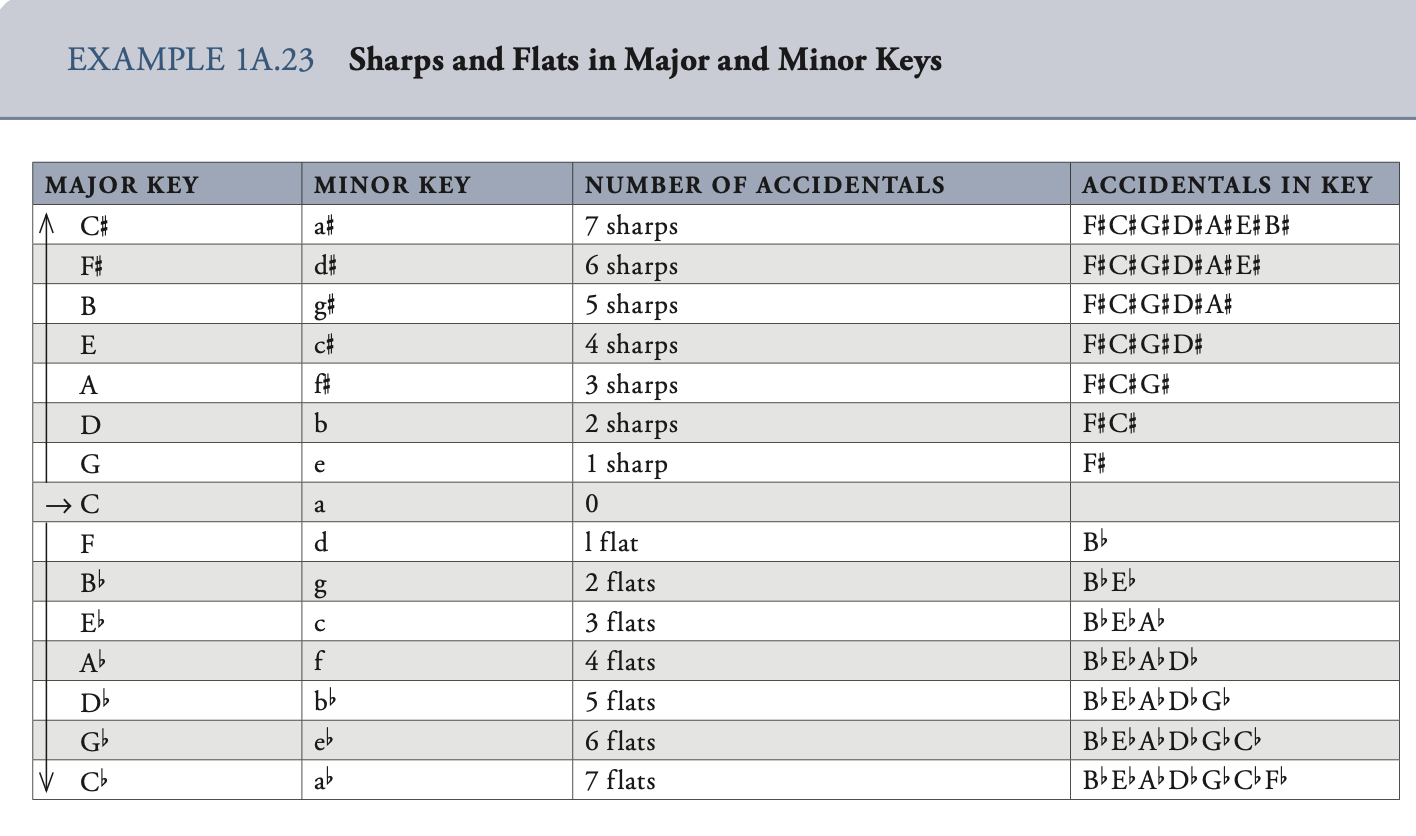
circle of fifths 五度圈
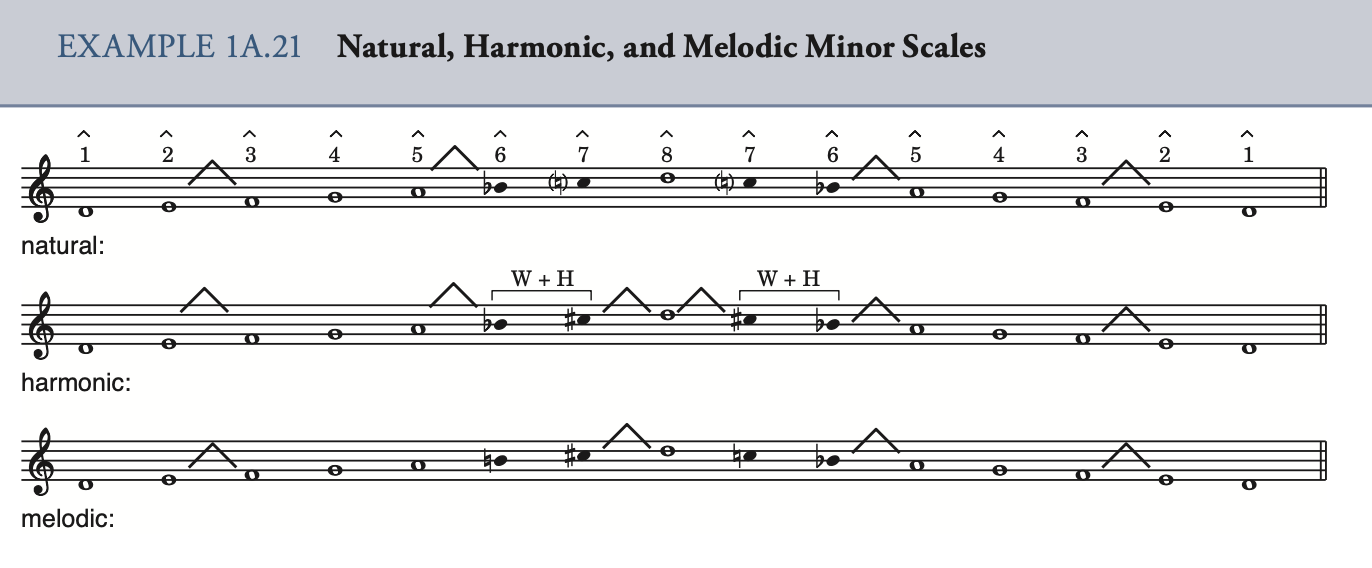
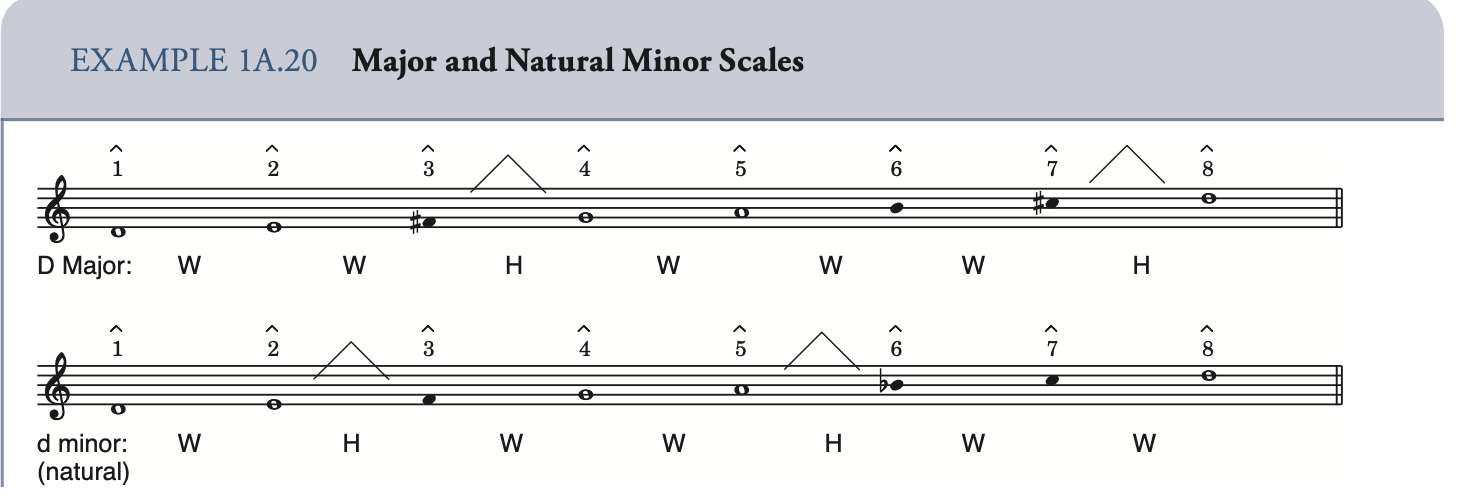

Melodic minor scale: 旋律小调音阶
Unison / prime 同度 一个音到它自己
melodic interval 旋律音程 先后弹奏两个音 harmonic interval 和声音程 两个音同时发响
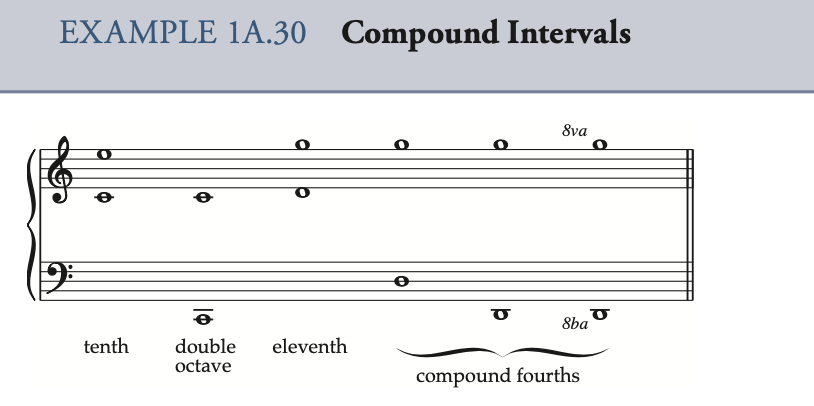
simple interval 单音程 小于等于一个八度的音程 compound interval 复音程 大于一个八度的音程

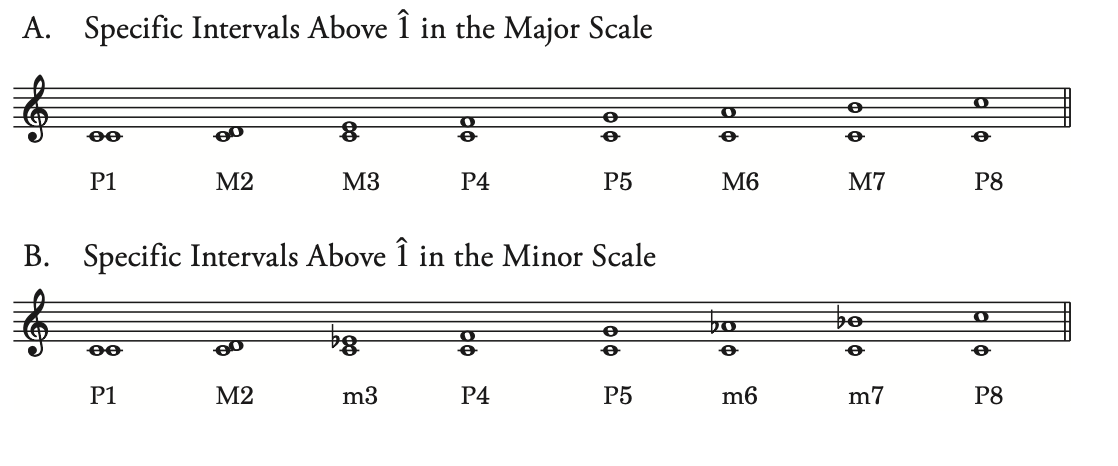
perfect (P) and major (M)/minor (m)
Perfect: 纯音程,在大小调都出现
Major/Minor 大音程 小音程
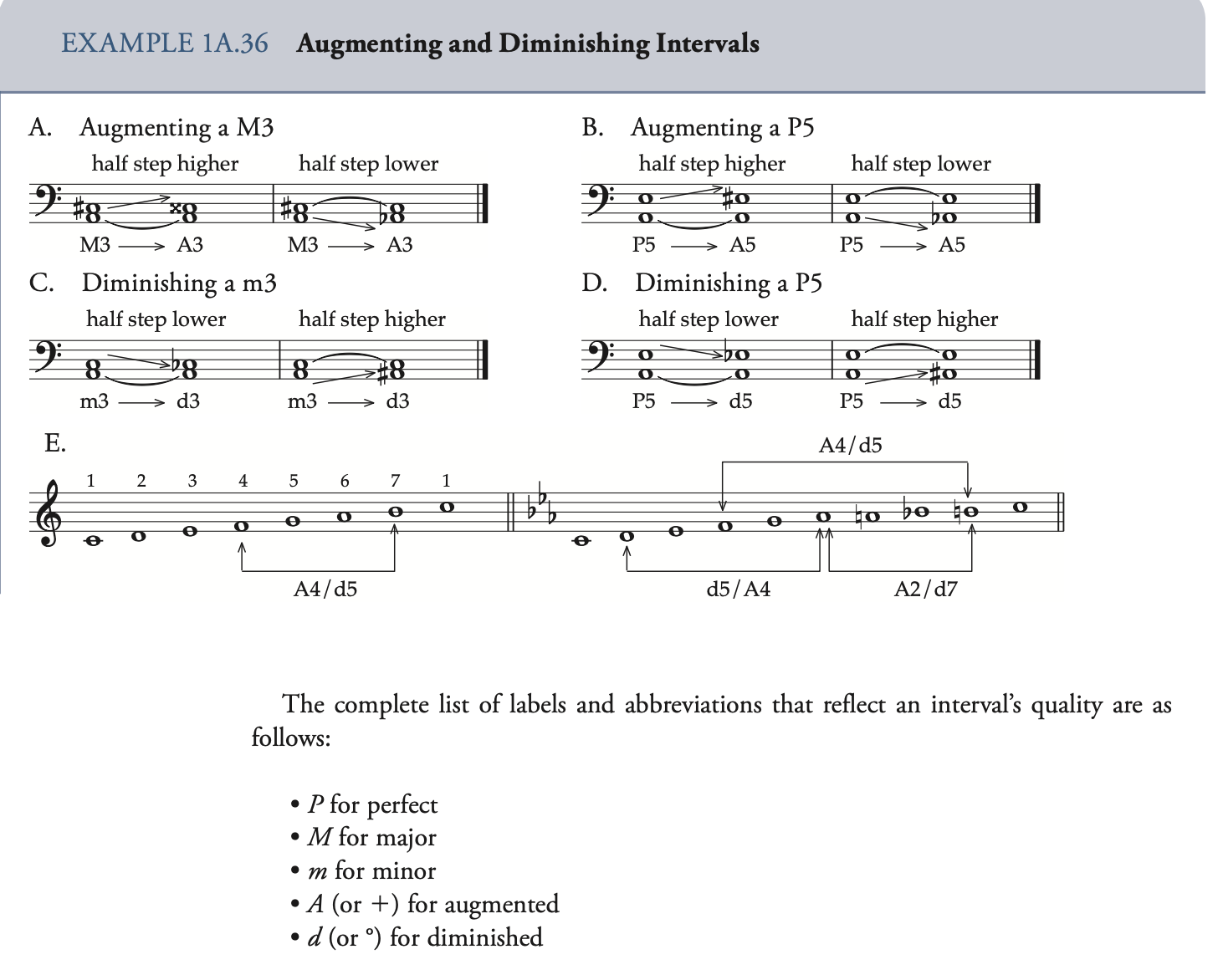
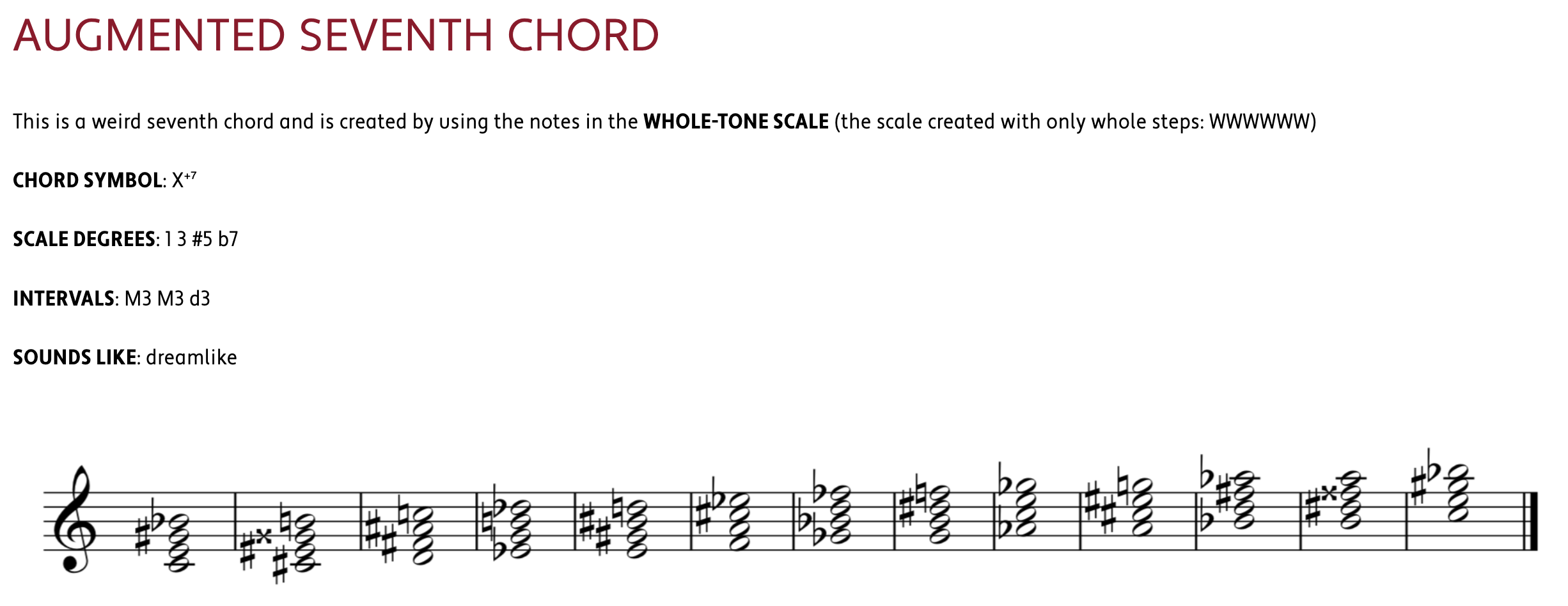
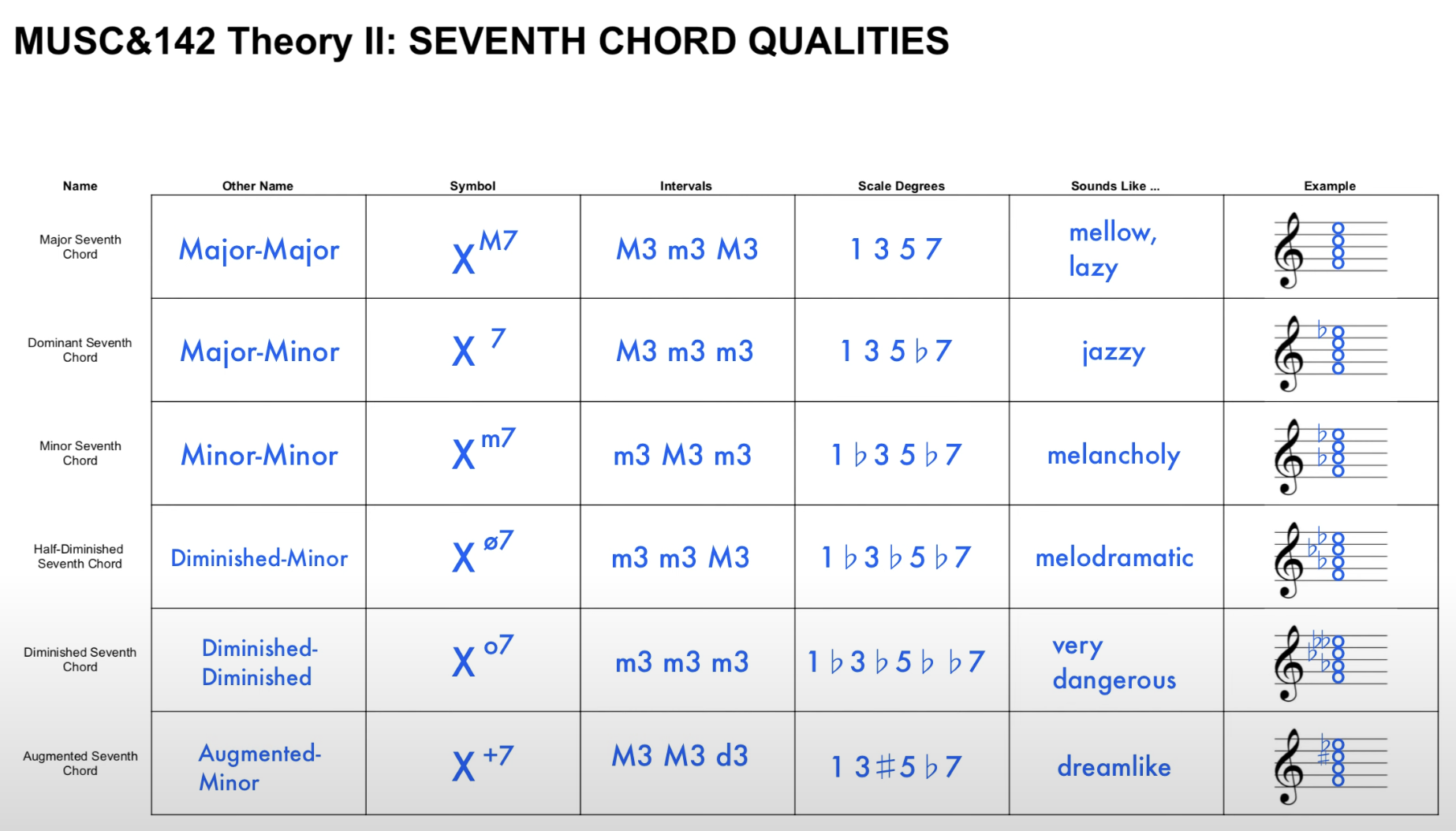
Augmented / Diminished 增/减音程
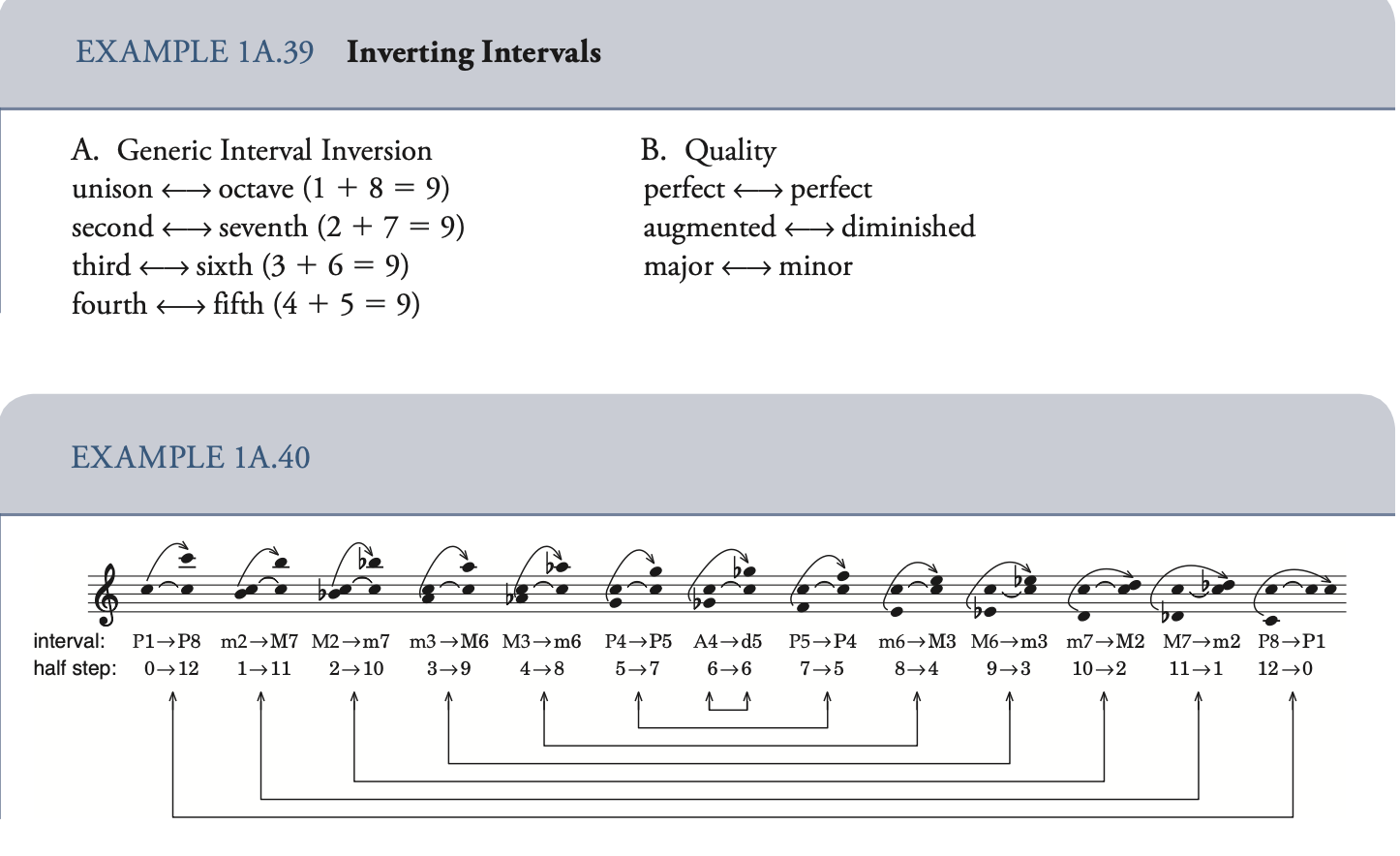
Interval Inversion 音程转位 把最低音移到8度以上
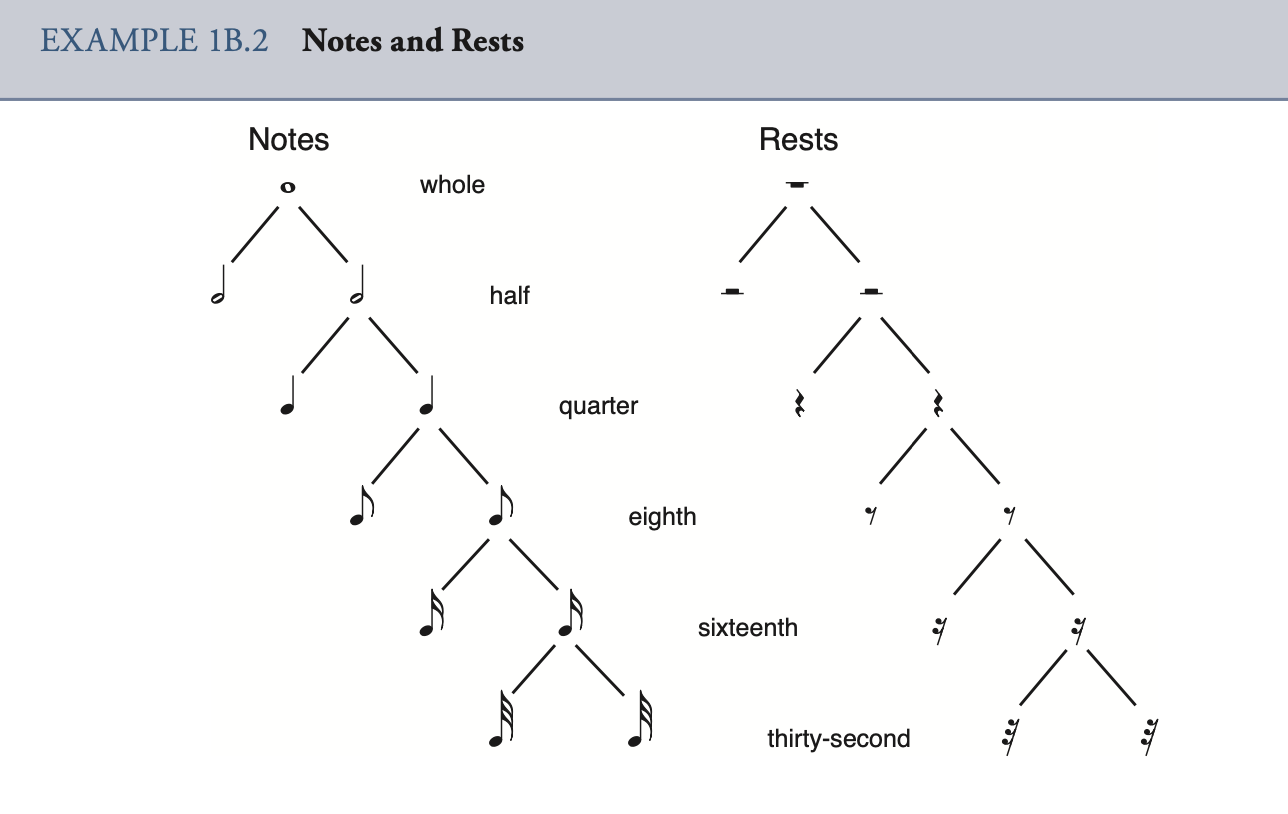
Pulse, Rhythm and meter
Dot 附点
Tie 延音线 相邻的音符
Slur 圆滑线 多个音符
Meter 拍子
The tempo of the piece is the speed of the pulse
Meter Signature 拍号
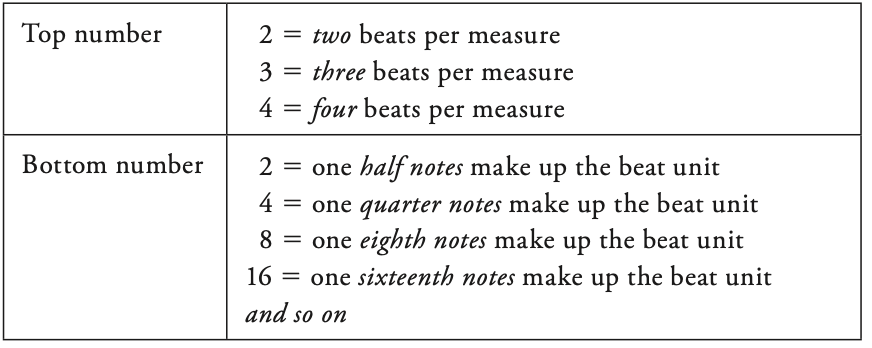
Triplet 三连音 合占一拍




Anacrusis 弱起
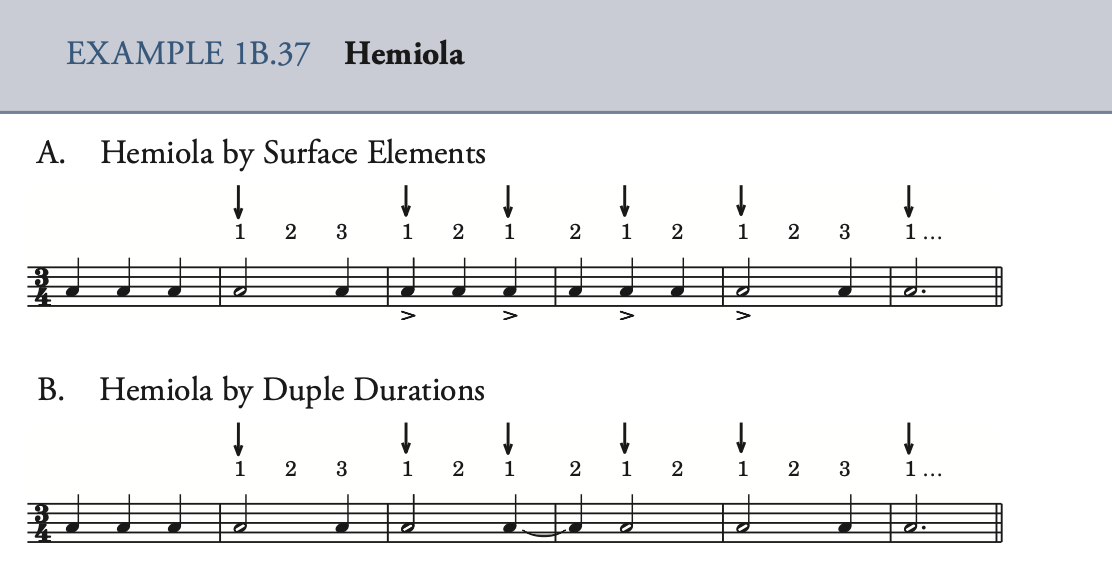
Syncopation 切分音
Harnessing Space and Time: Introduction to Melody and Two-Voice Counterpoint
counterpoint 对位
第一對位:單個音符間的對位(Note agianst note);
第二對位:兩個音符與一個音符間的對位 (Two notes against one);
第三對位:一組音符(泛稱,包含三個、四個或六個等音符構成的一組)與一個音符間的對位 (Four notes against one);
第四對位:延留音對位(Notes offset against each other);
華彩對位(Florid counterpoint,將以上四種綜合運用的對位手法)
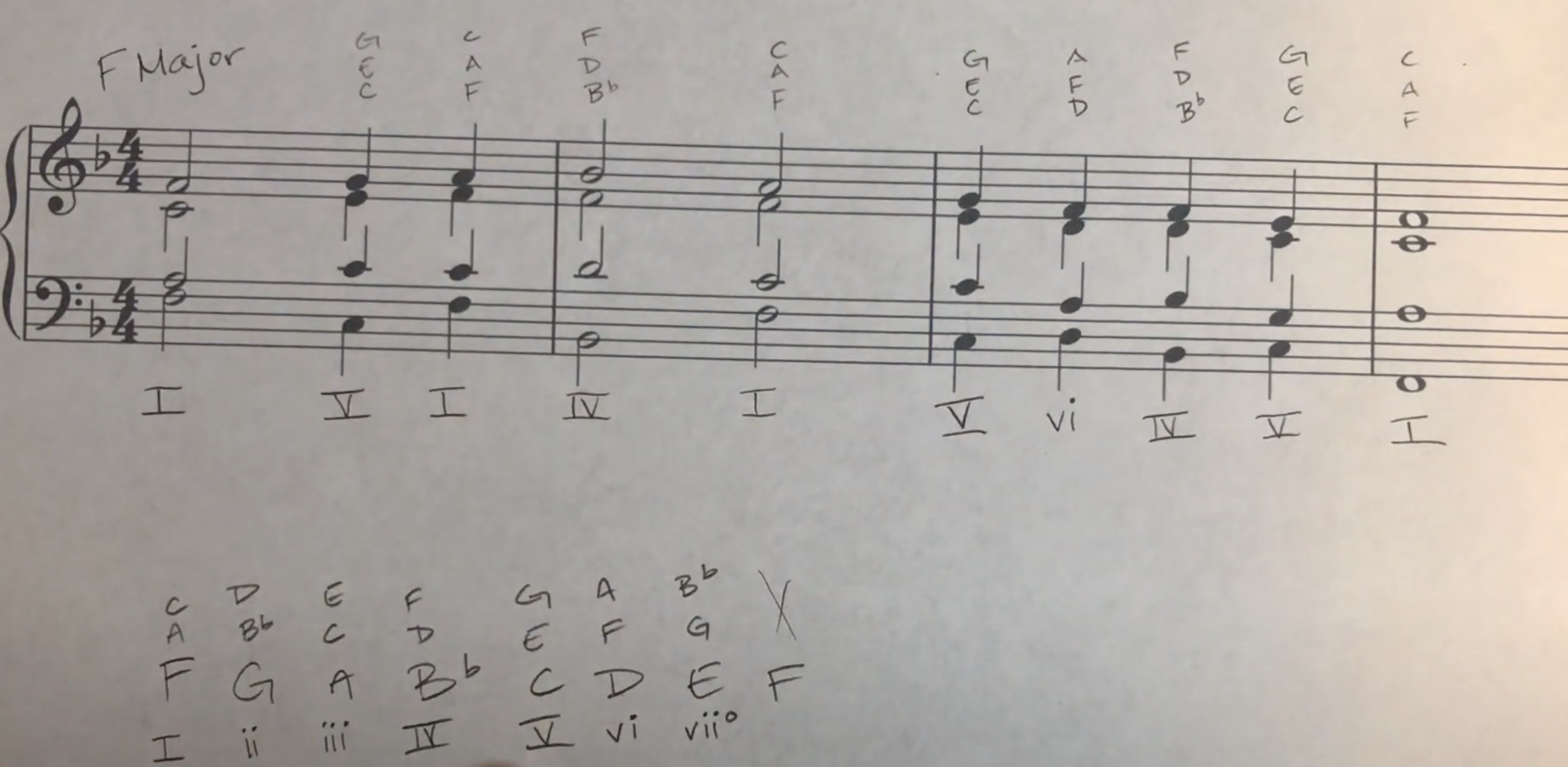

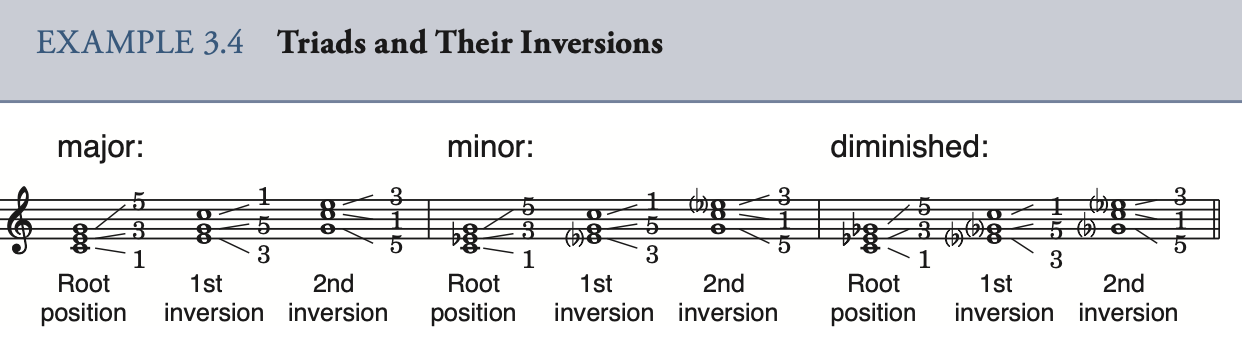
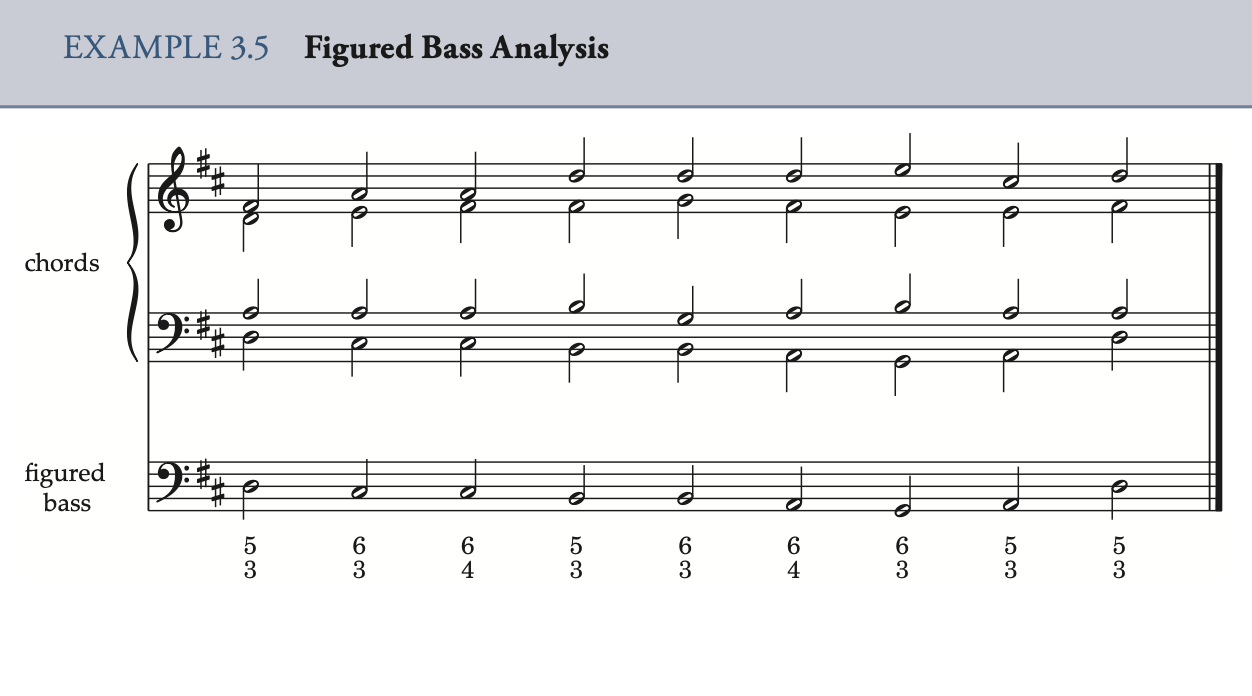
6 代表主音在最低音上面6度,第一转位

4 6 代表主音在最低音上面4度,第二转位

Most of the time, you should double the bass note somewhere above in the Tenor, Alto, or Soprano voice

polyphony 复调
Chapter 3: Musical Density: Triads, Seventh Chords, and Texture
Triad 三和弦
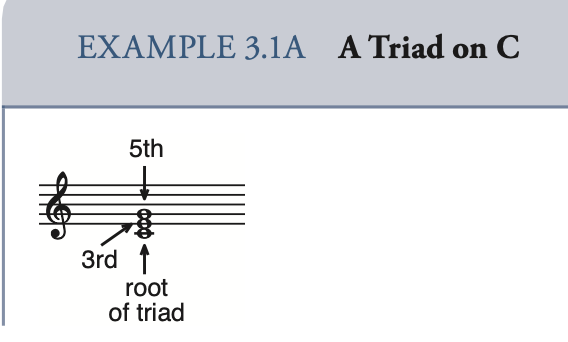

major triad 大三和弦 minor triad 小三和弦 diminished triad 减三和弦 augmented triad 增三和弦
root position 原位: the root is the lowest-sounding pitch, that is, if the root is in the bass
inversion 转位(complement)
When the third of the triad appears in the bass, the chord is in first inversion. When the fifth is in the bass, the triad is in sec- ond inversion
Figured Bass 数字低音,在巴洛克時期幾乎所有流派的音樂中都用作即興伴奏,但現代音樂中極少使用
harmonic analysis 和声分析
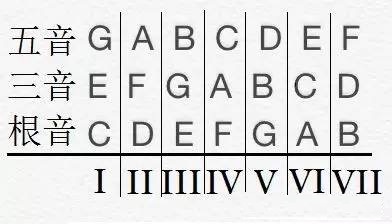
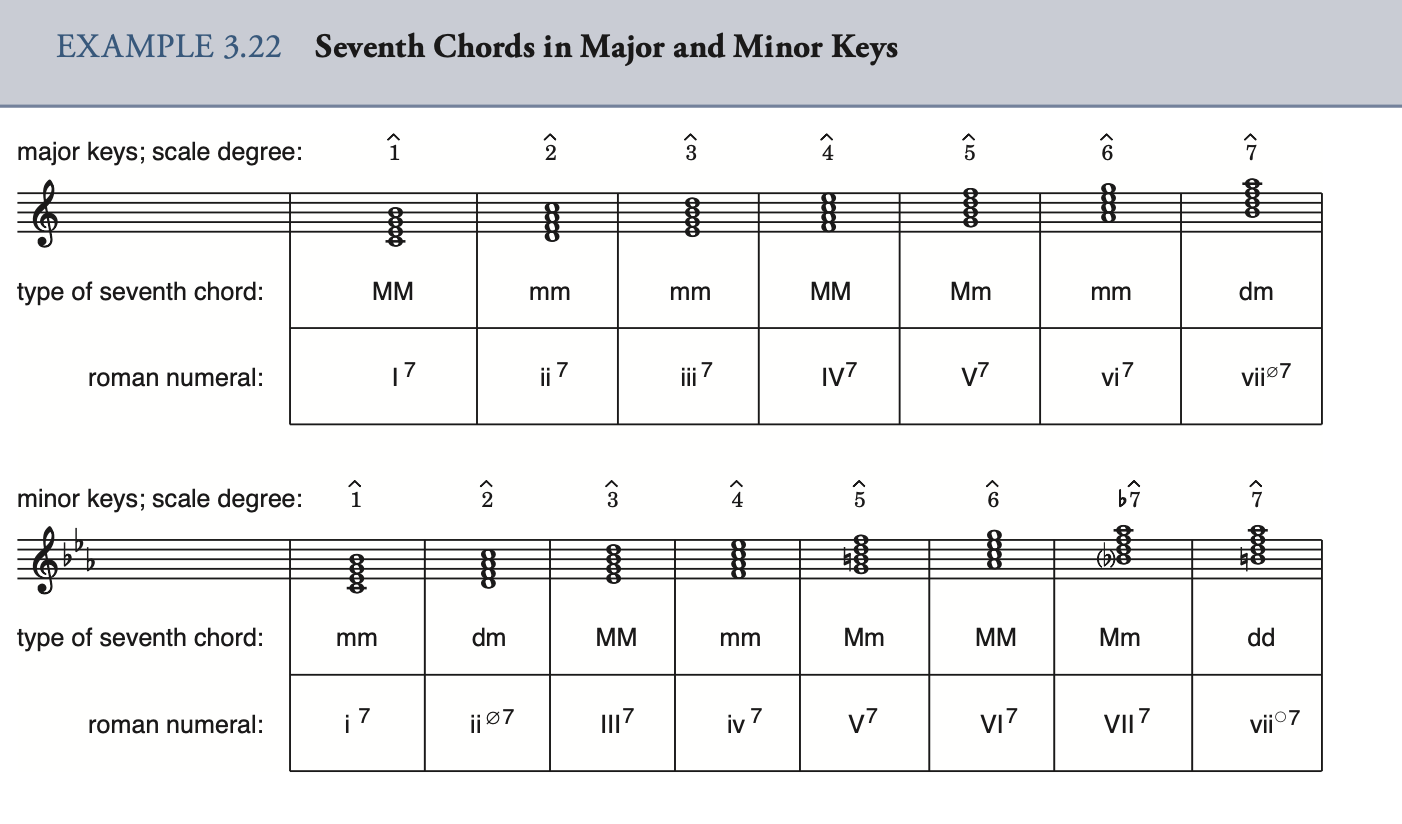
I = 一级(主和弦)
II = 二级(上主和弦)
III = 三级(中和弦)
IV = 四级(下属和弦)
V = 五级(属和弦)
VI = 六级(下中和弦)
VII = 七级(导和弦)
seventh chord 七和弦











ROLE OF VOICES: In general, the SOPRANO should serve as the melody (avoid awkward leaps, too much repetition, and too much pattern in the soprano voice), the ALTO and TENOR serve as harmony voices (finding common tones and stepwise movement from chord to chord) and the BASS serves as the bassline, usually leaping around from chord root to chord root or moving more melodically (MELODIC BASS) when inversions and non-chord tones are in play.
Chapter 4: When Harmony, Melody, and Rhythm Converge
consonant leap / chordal leap
https://kaitlinbove.com/nonharmonic-tones
arpeggiation 琶音
embellishing tones 和弦外音 若有一個音,且這個音所處的和弦中不包括這個音,則這個音被稱作和弦外音,或簡稱外音。

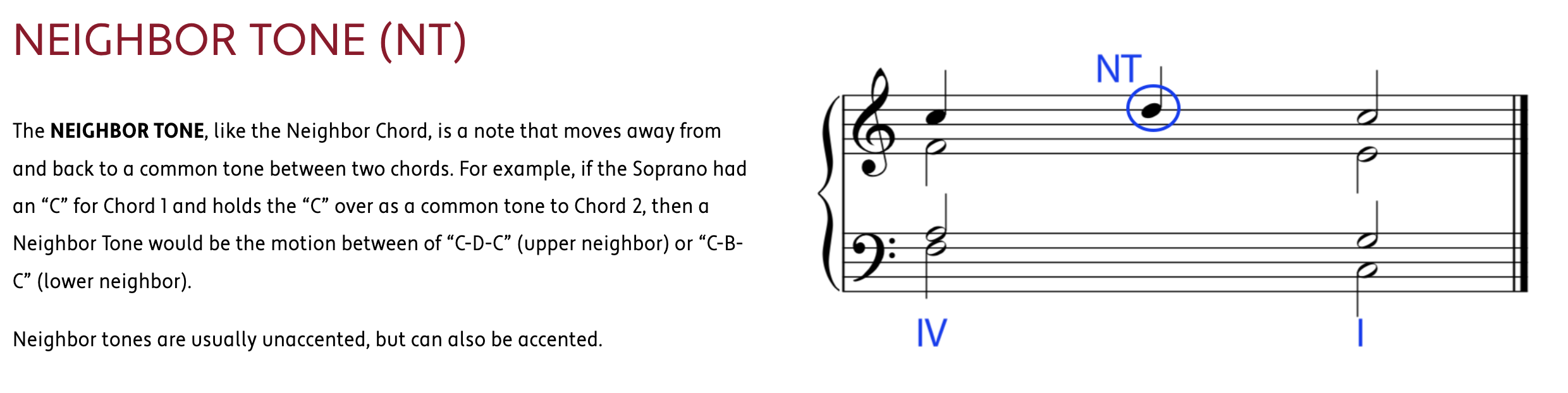
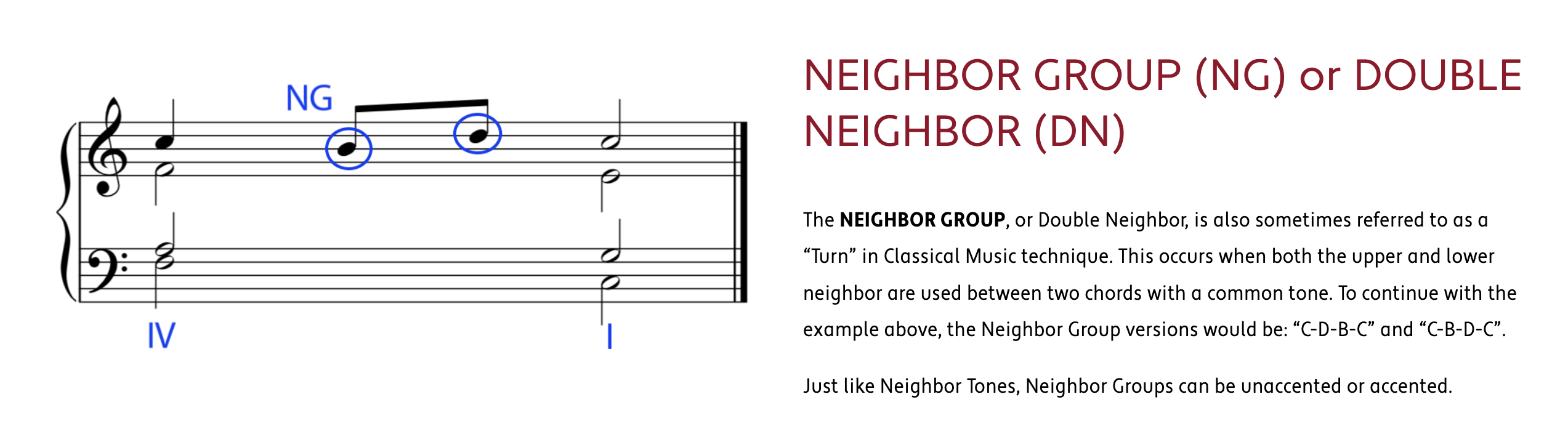

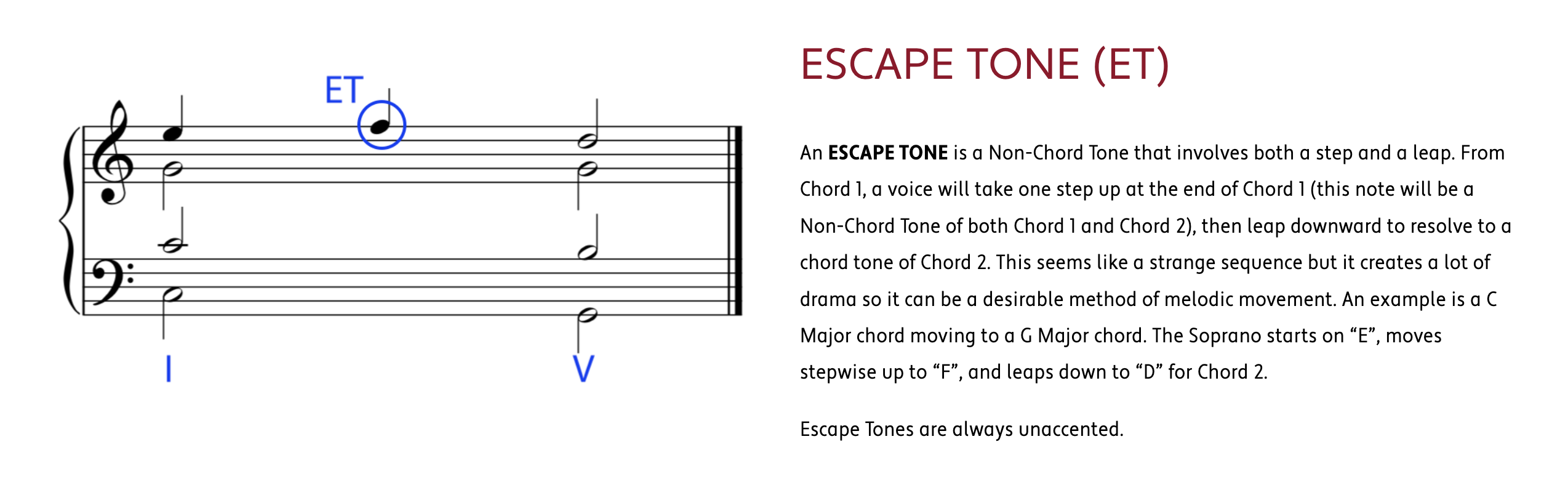
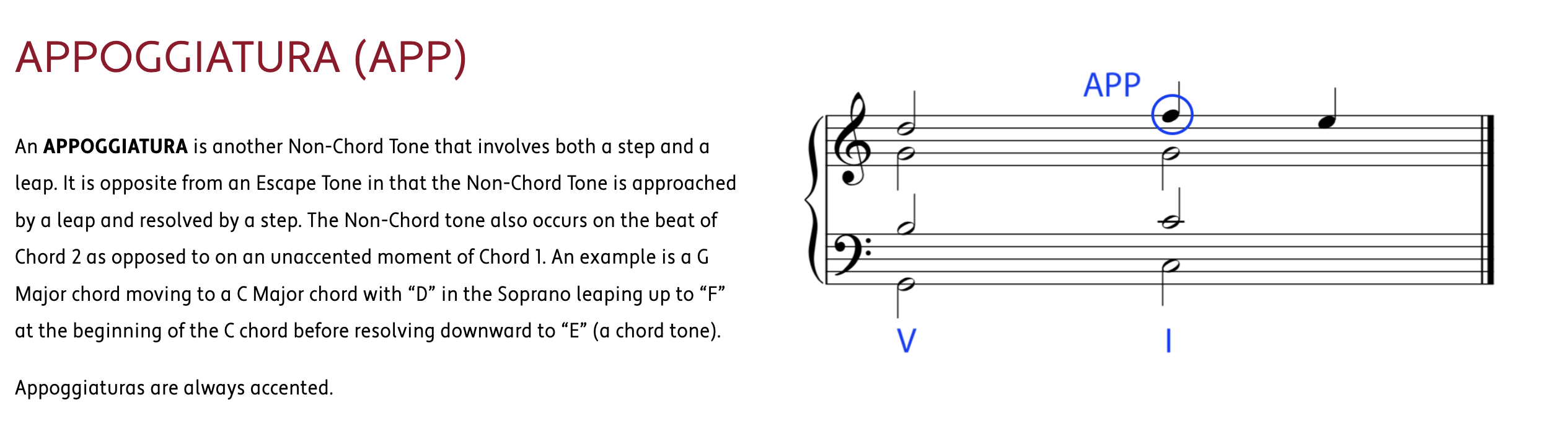
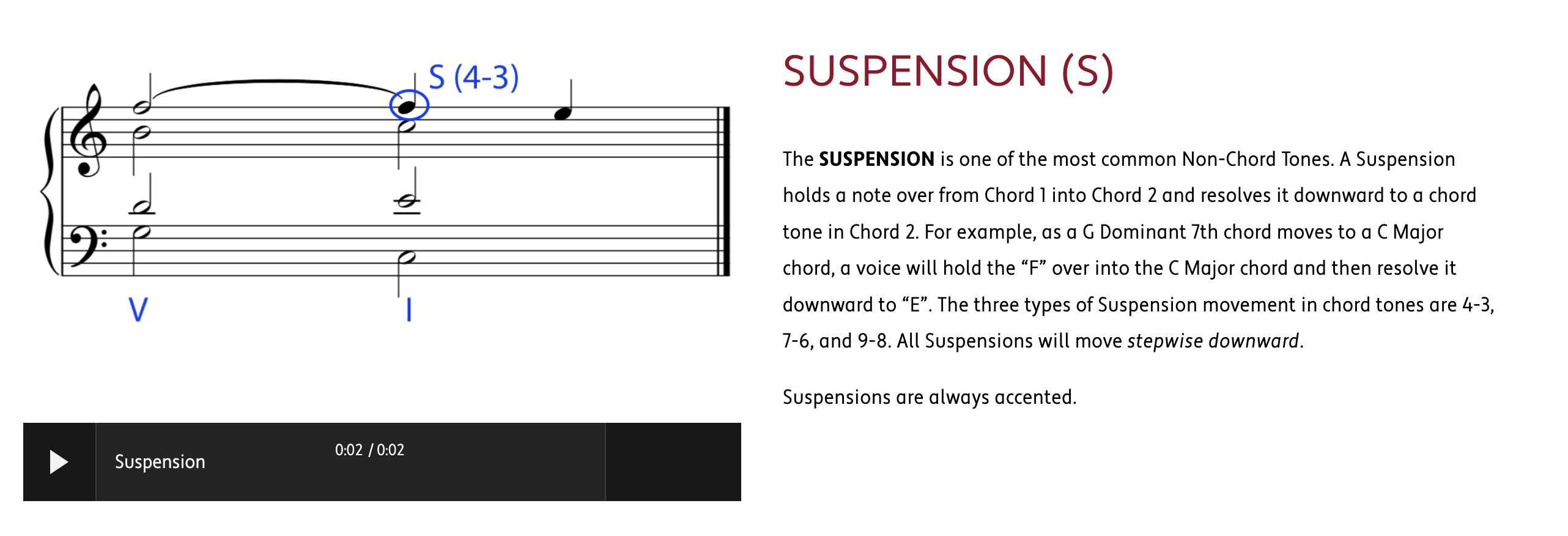
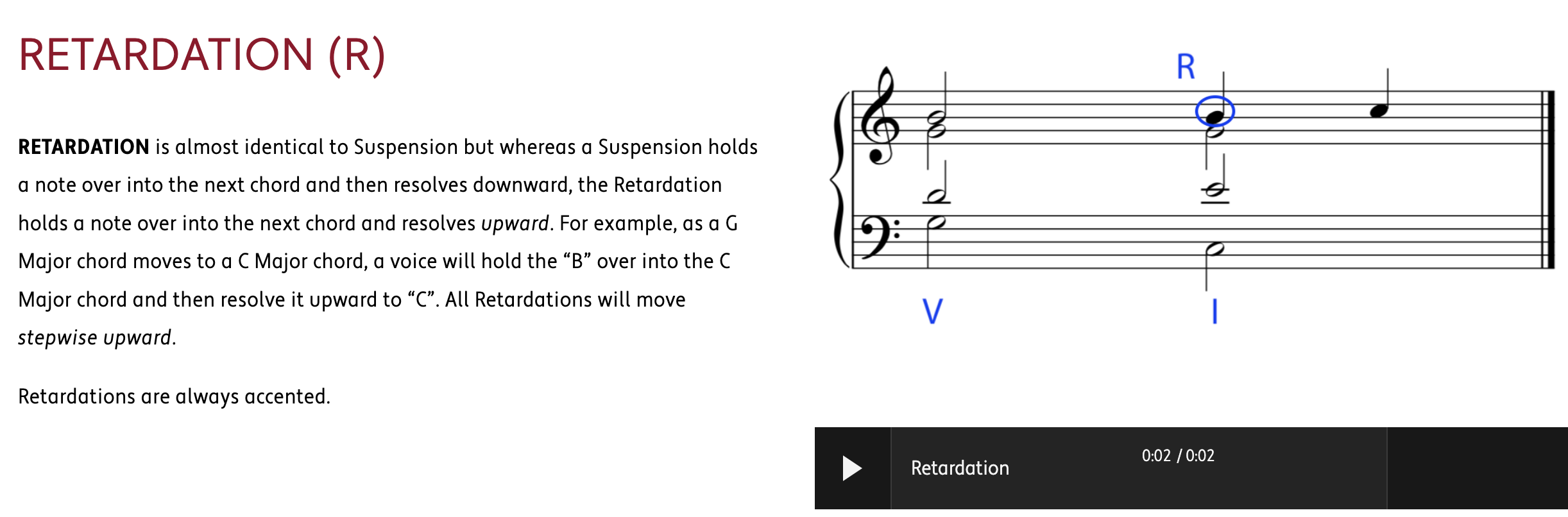
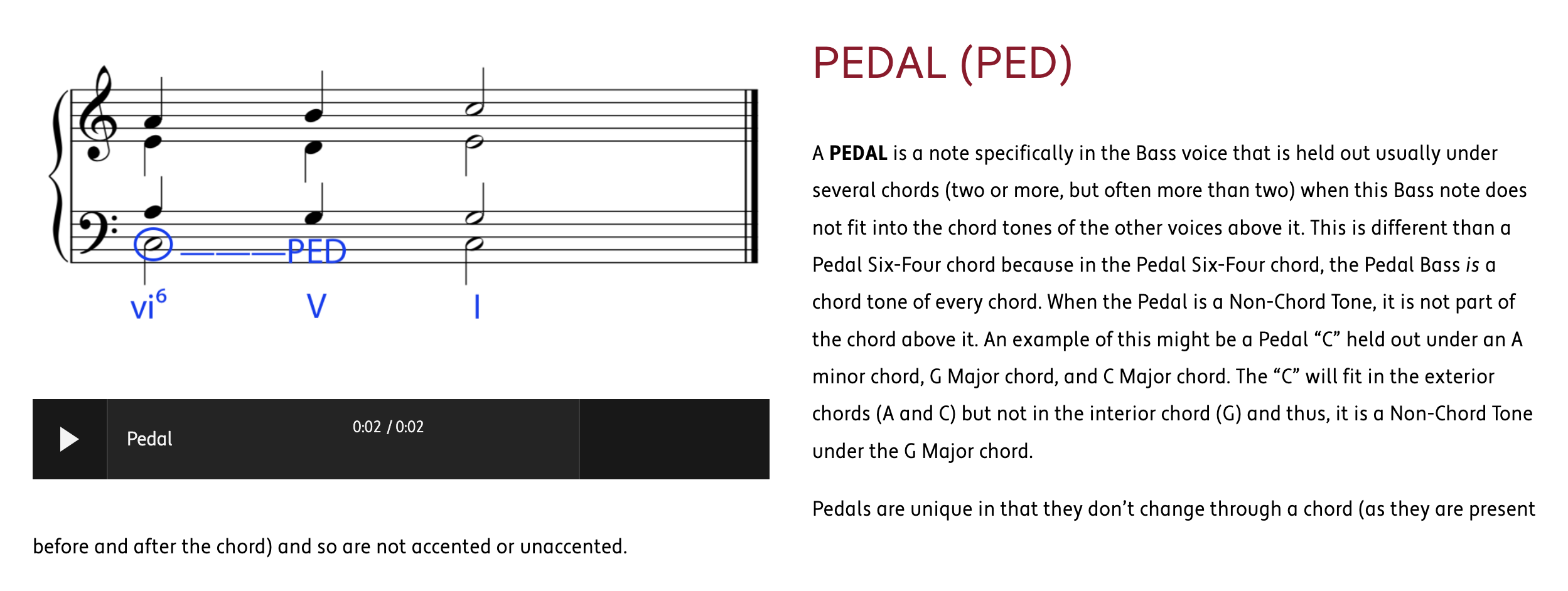
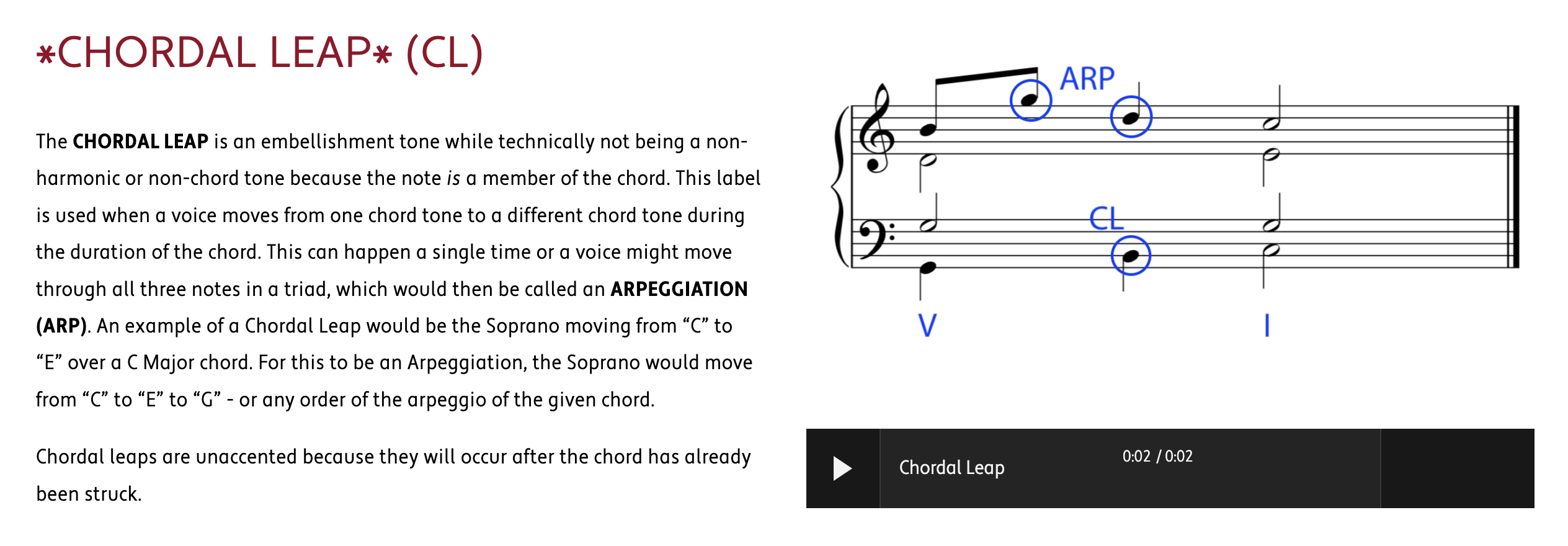
HARMONIC PROGRESSION (also known as CHORD PROGRESSION) is the logical movement from one chord to another to create the structural foundation and movement of a work in Western Classical Music.